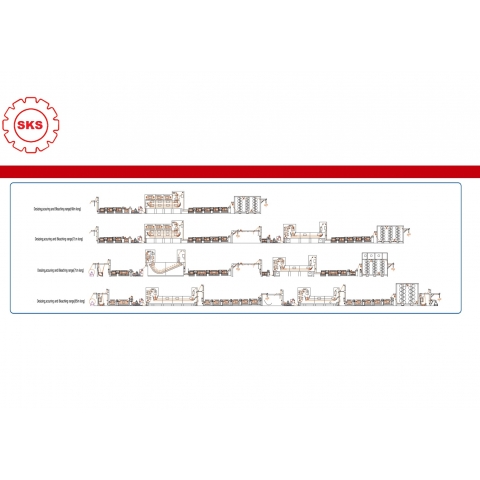
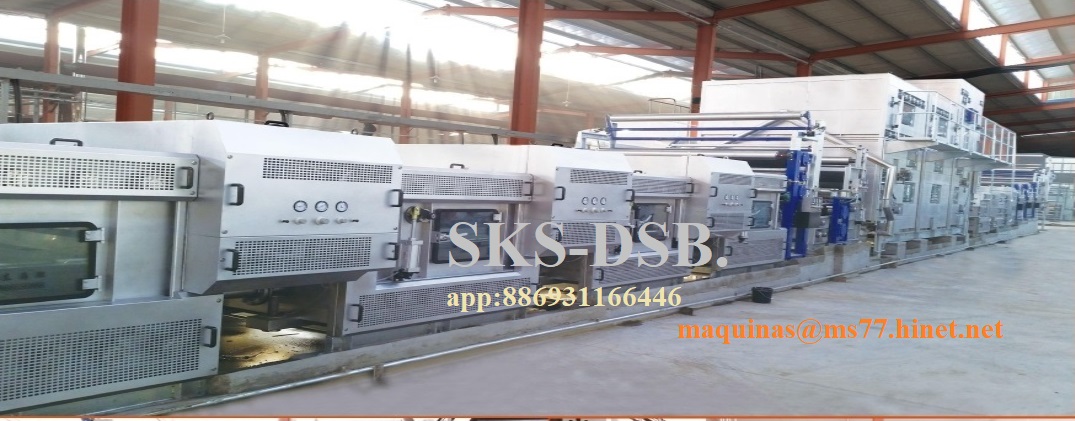
SKS-DSB2000 Desizing &Scouring &Bleaching machine line.
3 function(Desizing &Scouring &Bleaching) in one Machine Line.
A、Main technical data
- Machine width (roller width): 2000mm
- Designed speed: 10-120m/min
- Fabrics weight: 80-350gsm
- Water pressure: ≥0.2Mpa
- Steam pressure: ≥0.2Mpa
- Compressed air pressure: ≥0.4Mpa
- Driving system: PLC, inverter driving.
- Installed power: 135KW (around)

.jpg)
Desizing processes
Desizing, irrespective of what the desizing agent is, involves impregnation of the fabric with the desizing agent, allowing the desizing agent to degrade or solubilise the size material, and finally to wash out the degradation products. The major desizing processes are:
- Enzymatic desizing of starches on cotton fabrics
- Oxidative desizing
- Acid desizing
- Removal of water-soluble sizes
- Fermentative desizing
Enzymatic desizing
Enzymatic desizing is the classical desizing process of degrading starch size on cotton fabrics using enzymes. Enzymes are complex organic, soluble bio-catalysts, formed by living organisms, that catalyze chemical reaction in biological processes. Enzymes are quite specific in their action on a particular substance. A small quantity of enzyme is able to decompose a large quantity of the substance it acts upon. Enzymes are usually named by the kind of substance degraded in the reaction it catalyzes.Amylases are the enzymes that hydrolyses and reduce the molecular weight of amylose and amylopectin molecules in starch, rendering it water-soluble enough to be washed off the fabric.
Effective enzymatic desizing require strict control of pH, temperature, water hardness, electrolyte addition and choice of surfactant.
Oxidative desizing
In oxidative desizing, the risk of damage to the cellulose fiber is very high, and its use for desizing is increasingly rare. Oxidative desizing uses potassium or sodium persulfate or sodium bromite as an oxidizing agent.
Acid desizing
Cold solutions of dilute sulphuric or hydrochloric acids are used to hydrolyze the starch, however, this has the disadvantage of also affecting the cellulose fiber in cotton fabrics.
Removal of water-soluble sizes
Fabrics containing water-soluble sizes can be desized by washing using hot water, perhaps containing wetting agents (surfactants) and a mild alkali. The water replaces the size on the outer surface of the fiber, and absorbs within the fiber to remove any fabric residue.
Fermentative desizing
Fermentative desizing is defined as a fermentation process and involves the Generally Regarded as Safe (GRAS) microorganisms that have a high potential to produce enzymes; it is carried out via impregnation/padding methods, which provide online monitoring and accurate control. The method allows an economical process with low resource consumption and emission compared to the enzymatic method, it is considerably cheaper.
| Part name | Origin/Brand | Remarks |
| Inverter | Mitsubishi | Japan |
| PLC | Mitsubishi | Japan |
| HMI | Wenview | Taiwan |
| Low voltage electric parts | Schneider | France |
| Electrical cupboard | Guo Mao | China famous |
| Gear box | Guo mao | China famous |
| Bearing of washer | HWL | Japan |
| Bearing of padder | TMK | USA |
| Bearing of cylinder dryer | HWL | Japan |
| Tension sensor | China famous | |
| Air pneumatic parts | AIRTAC | Taiwan |
| Pneumatic cylinder | SMC | China famous |
| Rubber | Wuxi NO.2 company | China famous |
| Mechanical seals | Lianmin | China famous |
| Out ball bearing | Angsuan | China famous |
| Temperature control valve | Angle seat valve | China famous |
| Drying cylinder | 800mm | China famous |
| Rotary joints | Angxuan | China famous |
| Cylinder dryer Trap | Spirax |